|
Glacier Co. helps you to create your dream jewelry!
We produce one of a kind, custom pieces of art, that showcase your individuality and personality. Working with a certified gemologist for the stone selection and the most reputed of local goldsmiths for perfect craftsmanship; Every custom piece is made-to-order, so they are unique and of the highest quality. Without a large overheads of retail locations and display cases full of old inventory, Glacier Co. is able to offer the best wholesale prices while providing the most customizable and highest quality service. |
|
Education When purchasing a diamond, a little bit of knowledge can go a long way. Being familiar with a few diamond characteristics, knowing what to look for and a basic understanding of the terminology can ensure your diamond purchase is the right one. The most important characteristics of diamond grading have been broken down into four groups. Commonly known as “The Four C’s” of diamonds. They are as followed: |
|
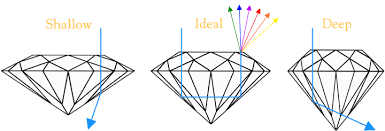
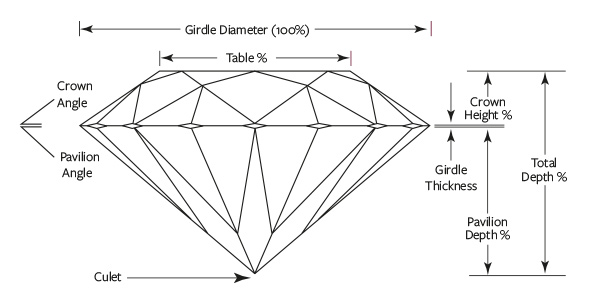
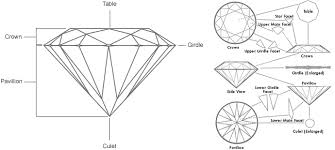
C U T Easily the most overlooked by inexperienced diamond buyers; Cut is the single most important and impactful trait of how your diamond comes to life. Cut does not refer to the shape of a diamond (ie round brilliant, princess, cushion cut etc.) but rather to the precise facet angles, symmetry and polish of which it was cut. When a diamond is cut correctly, light that enters the diamond is reflected from one facet to another, then dispersed through the table of the stone. If the cut of the diamond is too deep, light reflects once and escapes through the opposite side of the pavilion. If the cut is too shallow, light escapes through the pavilion before it can be reflected. This is known as light leakage and has a direct effect on that stones scintillation. (Scintillation is sparkle. Scintillation is the play of white and colored flashes of light seen when the diamond is viewed in motion. Viewable with the naked eye, scintillation is the life and brilliance of the diamond.) |
|
C O L O U R Diamonds can be acquired in just about every colour of the rainbow, but people typically prefer buying diamonds in the white range. However, the best color for a diamond is having no color at all! This is because diamonds that are colorless allow for the light to pass through them easily, resulting in greater light dispersion. This creates that great sparkle and rainbow coloured lights that we all love to admire. The colors of a diamond are graded from being totally colorless to light yellow. However, what you need to know is that the differences between one grade and the other are extremely subtle, and you need to have a trained eye with extensive experience to grade a diamond with regards to its color. Ie. If you put a D colour side by side with a E colour, it takes a trained eye to notice any difference. However if you put a E colour beside a H colour, the difference in colour becomes much more noticeable. |
|
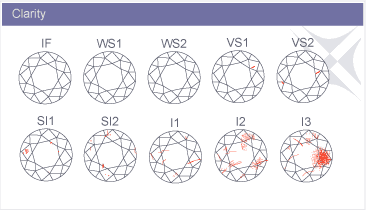
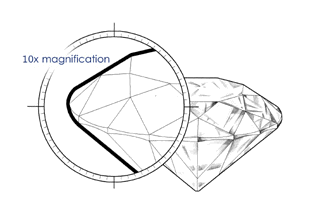
C L A R I T Y Since diamonds form under extreme heat and pressure, internal and external inclusions are common. These characteristics help gemologists separate natural diamonds from synthetics and simulants, and identify individual stones. Nearly every diamond has an inclusion or "birthmark". These inclusions can be either small or large, light or dark, few or many - like a fingerprint, each diamond is unique. When a diamond's clarity is graded, the value is based on the size, location and number of inclusions visible under 10x magnification. The following chart is used to help classify diamonds into various clarity grades: |
|
C A R A T Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its 'points' alone. For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point zero eight carats.' |
|
CERTIFICATE The unofficial “5th C” A diamond certificate, also called a diamond grading report, diamond dossier, or diamond quality document, is a report created by a team of gemologists. The diamond is evaluated, measured, and scrutinized using trained eyes, a jeweler’s loupe, a microscope, and other industry tools. A completed certificate includes an analysis of the diamond’s dimensions, clarity, color, polish, symmetry, and other characteristics, including a proper grade of Cut. A diamond certificate is the evaluation by a third-party, not by either the diamond buyer or seller. (i.e. Some diamonds dealers may inform you they carry only “In-house" certificates.) While there are many gemological laboratories around the world that can issue diamond certificates. It is GIA, based in the United States, that is considered to be the industry standard and is the most widely used and trusted name in the diamond trade. A lack of a certificate may be a clue that the diamond has been “enhanced” and the jeweler knows an inspection would reveal the diamond’s true value and condition. Here is an example of a GIA certificate; by looking closely you can identify all the properties needed for a quality diamond and all the areas we have just covered in this ‘Four C’s section. |